In the previous article in this series, I encouraged you to scrutinise your business goals and to decide if sourcing external funding will help you achieve those goals, without putting undue pressure on your business. We looked at funding for a short-term business boost – like buying inventory ahead of a peak season, hiring staff or launching a marketing campaign – and for long-term goals, like expanding into new markets or investing in an asset. I also played devil’s advocate and asked if there were other, more cost-effective ways to achieve these goals other than selling shares in your company or repaying a loan plus interest.
But if you’ve explored all options and are confident that money is the only thing standing between you and success, then deciding on the type of funding that best suits your business goals and financial circumstances is the next pivotal task.
Equity vs Debt funding
Business funding can be split into equity and debt funding. With equity funding, you raise money from investors in exchange for a portion of ownership in your business aren’t bound by hard repayment term. With debt funding, you are borrowing money without giving up ownership, but have to pay back the loan, with interest, within a specified time frame. The final option is to receive funding that you do not have to repay. This comes in the form of grants or competitions.
Let’s take a look at the nuances of the different small business funding options available.
Most of the funding options will require you to produce proof of your revenue and operating expenses. With the Yoco Business Portal, you can easily consolidate all your sales and transactional data.
EQUITY FUNDING
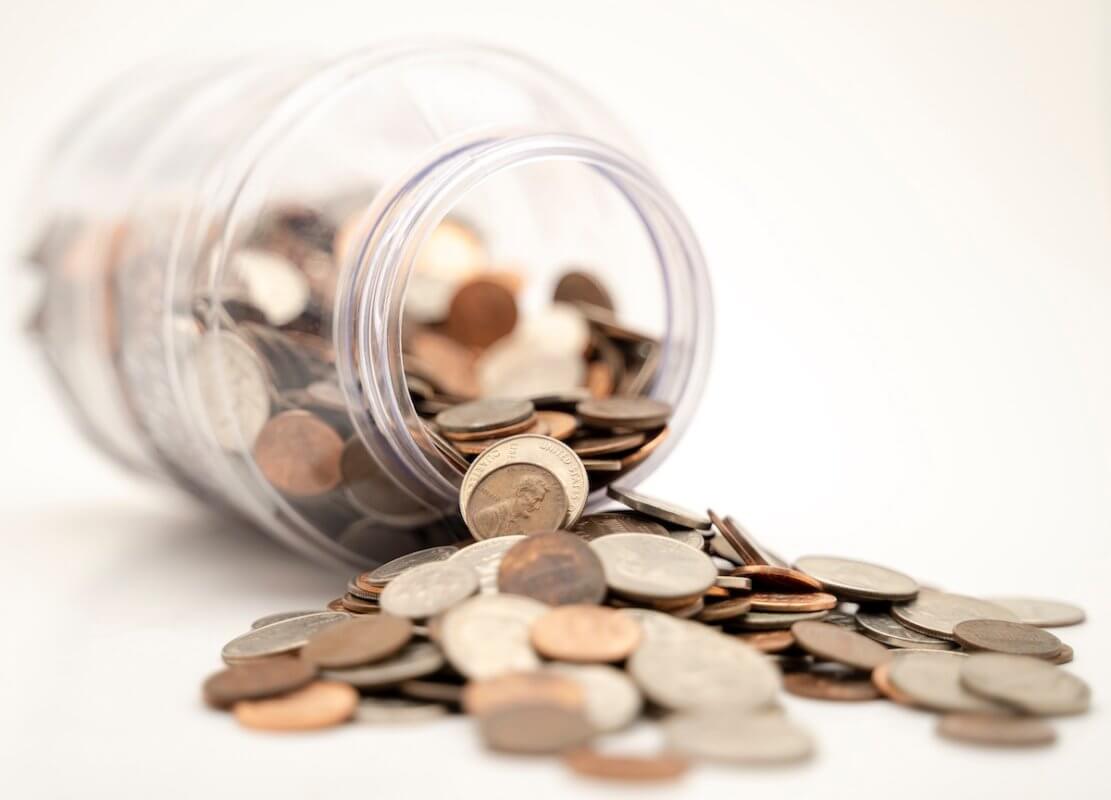
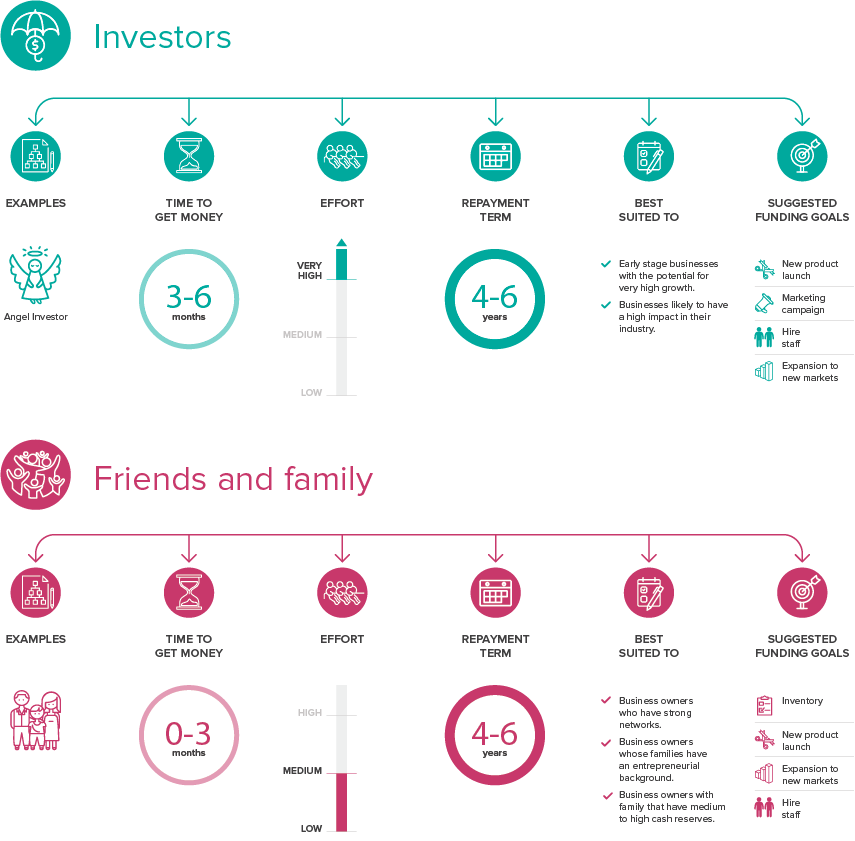
Angel and Venture Capital (Professional Investors)
Angel and Venture Capital (VC) investors offer you funding in exchange for a stake in your business. Both Angel investors and VCs fall under the “professional” investor category since they are more experienced and dedicated investors than friends and family. Both categories of investors expect high growth in their investment. They also bring significantly more capital to your business, but to do that; they would conduct a thorough assessment of all aspects of your business (a due diligence) before deciding to invest.
Angel investors are typically wealthy individuals who invest their own money in start-ups or small businesses, in exchange for a share in the business. They are motivated by the potential to make high returns on their money (In the form of sharing profits or the sale of their shares at a later stage). But they are often former entrepreneurs, who want to support entrepreneurship in general and do so by investing and mentoring other entrepreneurs.
Venture capital investors manage other investors’ money through a fund. The fund is tasked to make investments in a number of high growth, early stage businesses within a specified timeframe. VCs seek investments that can deliver massive returns and are less risk averse than traditional funds. However, to do that, they often take on a considerable stake in the business and in some cases a seat on the board.
Advantages:
- Opportunity to raise larger amounts of money compared to alternative options
- No need for collateral
- Many investors are serial entrepreneurs and can offer useful business advice, guidance, and knowledge
- No monetary repayments
- Flexible business arrangements (in most cases)
Disadvantages:
- Because investors expect shares in exchange for funding, you lose some control of your business
- The fundraising process is time-consuming and often grueling.
- Not a good fit if your business is not set up to be high-growth
- High competition among businesses competing for funding
- Some VCs come with complex investment structures, which requires some experience on the legal and financial side
Friends and family
Friends and family are often the first sources of funding you go to, especially when you are starting out. You can choose either an equity or a debt finance model. You can either agree to pay them back (hopefully with interest) or give them equity in your business. To help you decide, ask yourself if the person can give provide guidance or assist your business beyond funding. If so, giving them equity may be the right call. If you do not want the person directly involved in your business, then it’s advisable to opt for a loan. Just make sure you’re confident you will be able to repay them.
Advantages:
- Quick access to money
- Relatively low-risk funding option
- Gain the support of those closest to you
- Friends and family are less likely to turn down your request for finance if they have the money
- Repayment terms will be more flexible and low-interest, or interest-free
Disadvantages:
- If you run into difficulties with your business, this could impact your personal relationships
- You will feel responsible if your friends or family member loses money. This concern may make you more risk averse than you should be.
Quick tip: Even though you are working with someone you know, put a contract in place.
DEBT FUNDING OPTIONS
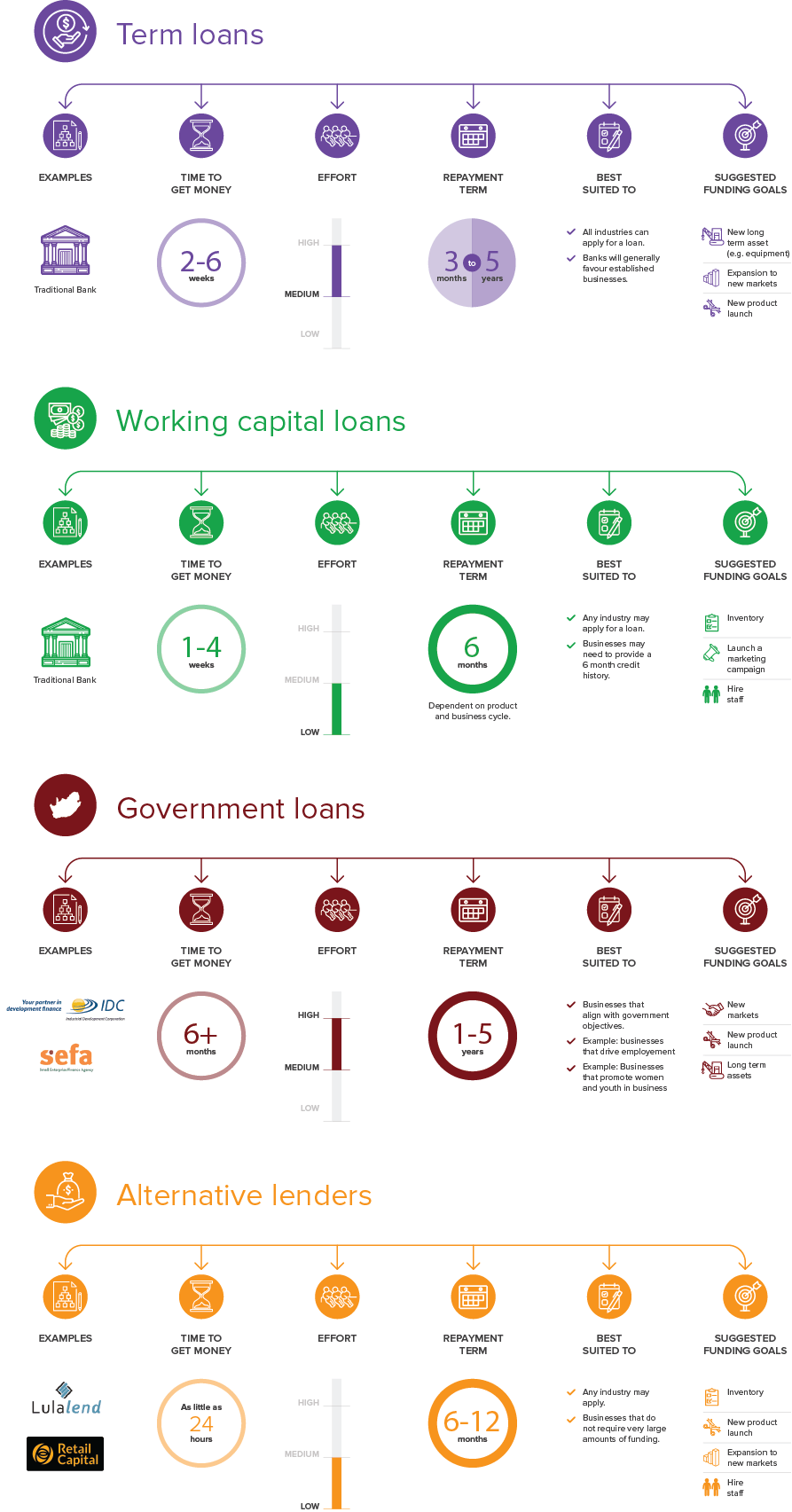
Bank loans (Term loans and Working capital loans)
When borrowing money from a bank, you generally have two options: a term loan, or a working capital loan. Term loans are best for long-term expenses like expanding into new markets or purchasing an asset. Working capital loans are ideal for short-term financial commitments, like hiring seasonal staff or buying stock ahead of a busy season.
Term loans are repaid in regular payments – generally monthly – over a set period – anything from three to 10 years. Term loans are subject to interest repayments, which can be substantial and are affected by economic fluctuations.
Working capital loans take the form of overdrafts, short-term loans (three to six months) or debtors funding, to fund the day-to-day running of the business and to cover immediate and short-term financial commitments.
Advantages:
- No need to sell shares in your business, so you maintain full control
- Among the most secure funding options
- Working capital loans are relatively straightforward products and are typically better options to alternative lending
- Working capital loans do not require collateral
Disadvantages:
- Bank loans are subject to interest rate repayments, which means you end up paying a lot more for the money you borrowed – especially if interest rates increase during the repayment term
- You may need to attach an asset to secure the loan
- It can be a long process and involves a lot of paperwork before you actually see any money in the bank
- If you default on payments, the bank could attach your assets
- Bank loans can be difficult to secure for start-ups that don’t have the necessary credit history or personal sureties and assets
Government loans
Government loans are issued by the Department of Trade and Industry and organisations like the Small Enterprise Development Agency. Unlike grants, government loans do need to be paid back.
There are a number of funding agencies in South Africa that support different business needs. The Land Bank, for example, is a good option if you need to invest in an asset for a farming business, and the Small Enterprise Finance Agency might be able to help you expand into other markets.
Advantages:
- Lower interest rates than bank loans
Longer or more flexible repayment terms
Disadvantages:
- Very strict qualification criteria
- The application and approval process can be long and frustrating
Alternative lenders
Alternative lenders are digital credit providers other than banks that offer financing to small businesses that do not qualify for a bank loan. These technology-driven businesses don’t have the infrastructure and operating costs on the scale that banks do, which allows them to offer loans at comparatively low-interest rates and with flexible repayment terms. Many alternative lenders promise fast turnaround times thanks to data-driven decision-making and transparent fees. This makes them an attractive funding option for small businesses that need to access finance quickly.
Examples of local alternative lenders are Lulalend and Retail Capital.
Retail Capital has an interesting operating model. The loan granted to you depends on your average monthly card turnover. If you’re using a solution like Yoco, you can quickly calculate your average turnover in the business dashboard. You repay the loan in daily micro-payments, calculated as a percentage of your earnings for the day. The percentage is agreed upon upfront so there are no unwelcome surprises at the end of the day and you can better manage your cash flow.
Lulalend offers six- and 12-month repayment options that include a monthly cost. Finance is granted based on the health of your business and your personal credit score.
Advantages:
- Access to finance is quick, with some lenders promising a turnaround of a few hours to a few days
- Little to no paperwork, as everything is done online
- Maintain full control of your business
- No assets required
- Transparent fees and flexible repayment terms
- Less stringent qualification criteria
- Simplified borrowing experience
Disadvantages:
- Potentially high or confusing interest rates
- Shorter terms and smaller loan amounts, depending on how much you qualify for
- Some alternative lenders may not be fully regulatedlo
UNIQUE FUNDING OPTIONS
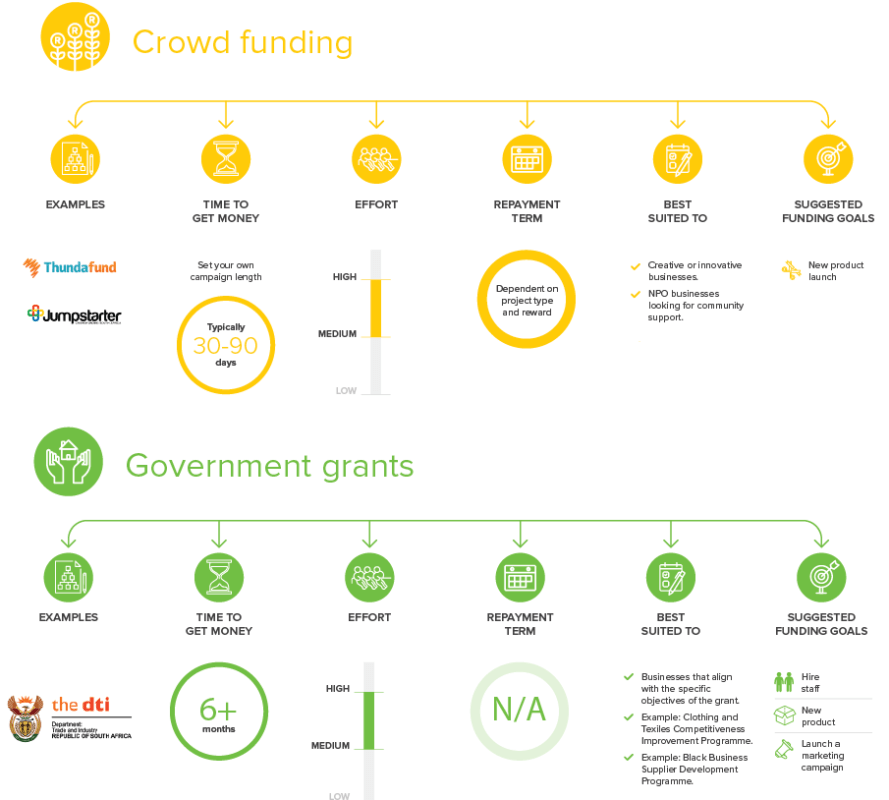
Securing funding that you do not have to repay can be a fantastic boost for your business. You could enter a small business competition, request donations if you’re an NPO or apply for Grants. Alternatively, you could look into crowd funding. This is where you can decide what you would like to offer sponsors in return for their contributions.
Crowd funding
You can finance your project or business venture by raising small amounts of money from lots of people who believe in your idea. Crowdfunding sites like Kickstarter, or South African platforms, like Thundafund and Jumpstarter, are ideal channels for connecting entrepreneurs and investors. The idea behind crowdfunding is that ‘every little bit helps’ and it works best for projects that require relatively small amounts of capital.
It’s important to remember that crowd funding does not mean free money and donors will expect something in return – free products or shares in your business, for example.
Advantages:
- Raise money quickly. If there’s demand for your product in the market, people are more likely to donate – especially if it earns them a discount on that product in return.
- Market your business at the same time. Crowdfunding campaigns are most successful when you leverage your social networks to reach more potential donors. You also have an opportunity to test market appetite for your product or service and get feedback on improvements that you can make before releasing it to the wider market.
- It’s free. Well, nearly. It’s free to set up a crowdfunding campaign, and there are no penalties if you don’t meet your goal in time. But if you do, a commission will be payable to the platform, which is generally in the region of 5-10%.
Disadvantages:
- Crowd funding can be very time consuming and resource intensive. For example, distributing your product to your backers after the campaign can take up a lot of time depending on the size of the base.
- If you’re offering shares in your business in exchange for money – which is less common in crowd funding – you could end up being beholden to thousands of inexperienced shareholders when it comes to making important business decisions.
There’s a risk that someone could copy your idea.
Government Grants
The South African government offers funding grants to small businesses, but these come with strict guidelines and qualification criteria. Grants are linked to government’s expressed goals and economic growth strategies, which could include – but are not limited to – the advancement of black economic empowerment, job creation, and economic development.
Say, for example, you want to expand your black-owned business into other markets. You could qualify for the Black Business Supplier Development Programme grant. To qualify, you must be a CIPC registered company or CC, must be 50.1% black-owned, must have valid tax clearance from SARS, and your turnover needs to meet a certain threshold.
This is one of many different types of government grants designed for start-up and growing businesses.
Advantages:
- Government grants do not need to be repaid and do not accrue interest
- You maintain full control of your business as you don’t need to give away equity
Disadvantages:
- Paperwork intensive
- Government may specify how you can spend the funds
- The application and approval process can take a long time to complete
Whichever funding option you choose, it’s likely that you’ll have to produce proof of your revenue and operating expenses, especially when applying for funding with banks or investors.
Securing the funding
Once you know which funding option you want to go, you need to start preparing. Most of the funding options will require you to produce proof of your revenue and operating expenses. With the Yoco Business Portal, you can easily consolidate all your sales and transactional data. It is a great tool to have when meeting with investors as it allows you to show sales and performance trends over time. This is one less thing you will have to worry about.



